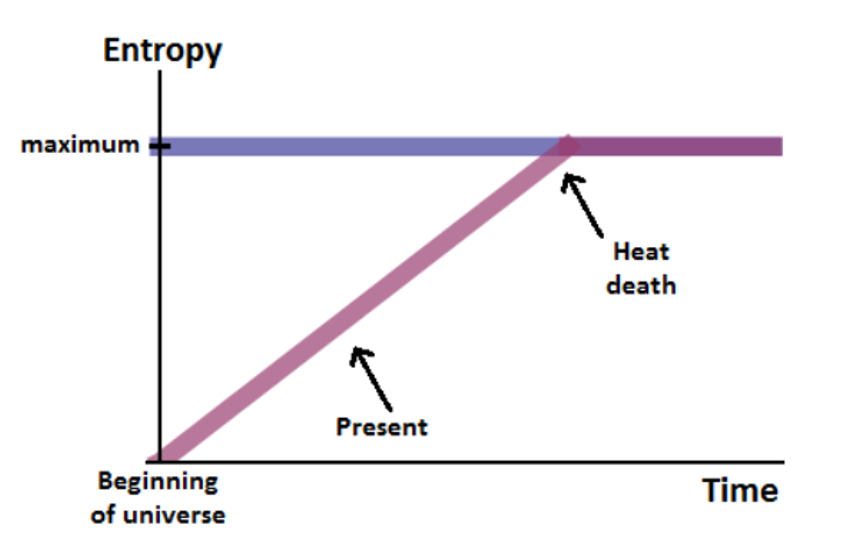
The Big Bang singularity is the proposed event when everything came into existence: all energy and matter. Thermodynamics (the scientific law of increasing entropy), says that over time, hot temperatures head toward colder (energy is not destroyed but is dissipated into the closed system). As an example a hot cup of coffee eventually becomes room temperature. In our universe “room temperature” of deep space is very cold at absolute zero –459.67°F. Thermodynamic laws equally apply to our universe because we are in an isolated system: a single universe. It is a very large system but it is a system nonetheless. The action of thermodynamics are understood by scientists and are illustrated by the so called “heat death” or “deep freeze” of the universe.
Cosmologists founded in naturalistic worldviews were shocked to discover that based on observations of Edwin Hubble in 1929 that the universe had a beginning and it was not infinite as had been believed since the early 1800’s.1 This was a bitter pill and much too close to the biblical account of creation– they preferred the infinite universe theory much better. In fact, the term “Big Bang” was originally coined by Fred Hoyle and was fully intended as being derogatory toward the theory he disliked his entire life.2 Later, in 1979 Alan Guth identified that the universe had a flatness or inflation problem.3 Also called the Horizon “problem”, the phenomena caused the universe to appear the same form where ever the observer was located. This too was problematic tied to the explosion and the subsequent expansion of the universe immediately after the Big Bang.
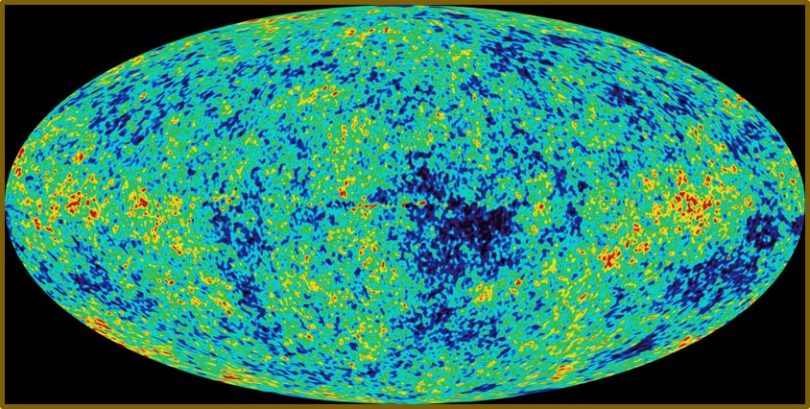
Finally, after obtaining background radiation images they found the presence of uniform radiation was evidence of a younger universe or the universe must have expanded even faster then originally calculated. The more precise perimeters discovered caused the Big Bang Theory to head toward mathematical absurdity. Other cosmologists recognize that the mass required at the singularity would have certainly fallen into a Black hole.
Cosmic background radiation (provides evidence of uniform) temperatures throughout the observable cosmos. This is a problem in standard Big Bang cosmology. According to the Big Bang Theory, up until about 300,000 years after the beginning of the universe, the photons (light) in the background radiation would have been bounced off the electrons in the hot plasma that filled the entire universe. At that point the universe would have cooled enough for electrically neutral atoms to form, releasing the background radiation.” (This is obviously not the case).
“This (background radiation gives) us a picture of the universe at around 300,000 years of age..requiring very precise initial conditions…very precisely fine-tuned initial explosion.”
Meyer, Stephen C “Signature of the Cell” 2009 p.500
The background radiation of the universe indicates a much younger universe then the supposed 13.8 billion years supposed as being less than 300,000. These ages are still much higher than the dates expected by Young Earth Creationists. We must remember that the mental gymnastics of The Big Bang Theory are designed to get the evidence of the universe (round peg) to fit the theory (square hole). That is why such matters are what cosmologists call “problems”. The Horizon or Flatness “problem”. The inflation “problem”. The background radiation “problem”. The massively precise math needed to make the Big Bang possible “problem”. The mass at the singularity black hole “problem”. However, to Creationists we have no problems with any of these issues. After all, when cosmologists attempt to hammer they round peg into the square hole we recognize that these “problems” are not our concern– they are theirs! We know where the universe came from– God created it!
LIMITATIONS OF THE BIG BANG THEORY
While the Big Bang theory can successfully explain the cosmic microwave background radiation and the origin of the light elements, it has three significant problems:
The Flatness Problem:
The geometry of the universe is nearly flat. However, under Big Bang cosmology, curvature grows with time. A universe as flat as we see it today would require an extreme fine-tuning of conditions in the past, which would be an unbelievable coincidence.3
The Horizon Problem:
Distant regions of space in opposite directions of the sky are so far apart that, assuming standard Big Bang expansion, they could never have been in causal contact with each other. This is because the light travel time between them exceeds the age of the universe. Yet the uniformity of the cosmic microwave background temperature tells us that these regions must have been in contact with each other in the past.3
The Monopole Problem:
Big Bang cosmology predicts that a very large number of heavy, stable “magnetic monopoles” should have been produced in the early universe. However, magnetic monopoles have never been observed, so if they exist at all, they are much more rare than the Big Bang theory predicts.3
1 https://skyserver.sdss.org/dr1/en/astro/universe/universe.asp
2 https://academic.oup.com/astrogeo/article/54/2/2.28/302975