I praise you because I am fearfully and wonderfully made; your works are wonderful, I know that full well.”
Psalm 139:14
Careful study of evolution has uncovered, in light of multiple radiations of widely diverse organisms over an assumed millions of years, with perhaps a few thousand new species identified, yet, all the trials grow cold before even reaching a new animal classification level of family. Basically, we do not see any evolution as anticipated by common ancestry or descent of species.
What we find is the same species diversifying into the same species– that is it.
George Barlow was the lead researcher on African Cichlids found, “minor changes “plentiful”, yet basic innovations are completely lacking.”
The Cichlid Fishes: Nature’s Grand Experiment in Evolution
George W. Barlow, Author, George Christopher

Why is unguided evolution proficient at filling environmentally based niches with new species but is stuck in the mud before any new fundamental new biology is produced?”
Experiments (under laboratory conditions) found that bacteria “gained” a new “function” to digest citrate in a oxygen free atmosphere. Sounds like evolution right? Well, data shows that this occurred due to degraded and deleted segments of DNA genetics. Once the organism is forced to make such genetic modifications as to survive, they cannot be undone because the genes are permanently lost. Then, under unique circumstances, reproductive DNA function of alleles freezes such changes in place. Thus holding the havoc wreaked by random mutation locked in place by natural selection. Indicating a mechanism that keeps Darwinian evolution from producing higher classifications even such meager changes as species to genus. These changes do not and cannot occur due to these observed mechanisms.
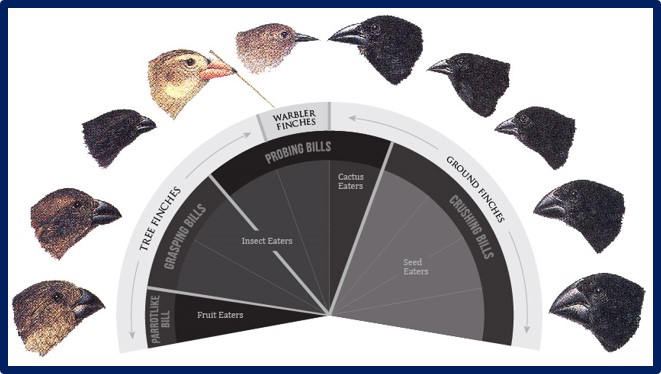
Darwin’s finches identified variation in body length and beak characteristics with a difference of 5-6 percent. In 1977 a documented drought killed 85% of the smaller birds with smaller beaks due to plants remaining dormant and not giving off food. The hardier birds reproduced, those with larger beaks that could break larger seeds. Since researchers have been collecting data one species had disappeared because it began breeding with another species and now is gone, therefore the larger tree finch disappeared from the island.1
A new study shows that approximately six different finches identified on the island are actually determined as being different species although all are finches and can interbreed. It seems such “interbreeding” has been occurring for thousands of years, thus, it is reasoned, they have never been able to fully (evolve) emerge into truly new species.
The observed drought proved Darwin’s idea that these changes occur to slow to see was disproved— they occurred instantly within a few years. Then populations resumed. The birds that died off actually passed with less genetic information. The “evolution” which occurred during the drought of 1977 was “biologically trivial”.
The most important finding of all the research was the fact that the remaining populations had gained literally nothing new genetically. Sure, population sizes changed, some new infusion of variation although likely nothing completely new. Such “new” mutations occured due to and from preexisting DNA code. It has been identified that some genes behave as “master controllers” turning on various proteins to encode (although the “how” and “why” remains a mystery).
New studies clearly demonstrate such molecular changes do account for small scale adaptation but data points decisively that these changes have strict limits on fundamental biological change as driven by random spontaneous mechanisms. Essentially allowing for variation within offspring of the same genus or species but does not extend to family of higher.”
Michael Behe “Darwin Devolves” page 142-143
In 2015, after DNA sequencing over 120 individual finches of various species a half dozen master controller sequences were found that pointed to blunt beak and pointed beak. The ALX1 gene consisting of 326 amino acid protein chain. The difference between blunt and pointed beaks were a mere 2 letters. Surprisingly, the computer analysis classified this protein variance as “damaging”. It was determined that this genetic mutation did not occur due to or during the 1977 drought but originated when the finches first arrived to the island. Therefore, this process has held over many generations, maintained as a beneficial mutation, counterintuitively, generated by damaged genetics.
Therefore, the differences of beaks were due to damaged genes, a loss of genetic information, potential loss of function, and notably less genetic information.

Even Polar Bears have been determined to have gathered many of their unique characteristics such as white fur color and high fat metabolisms as damaged genes. Just as the beak size worked for the survival of these birds it also worked for Polar Bears.
1 Michael Behe “Darwin Devolves”


