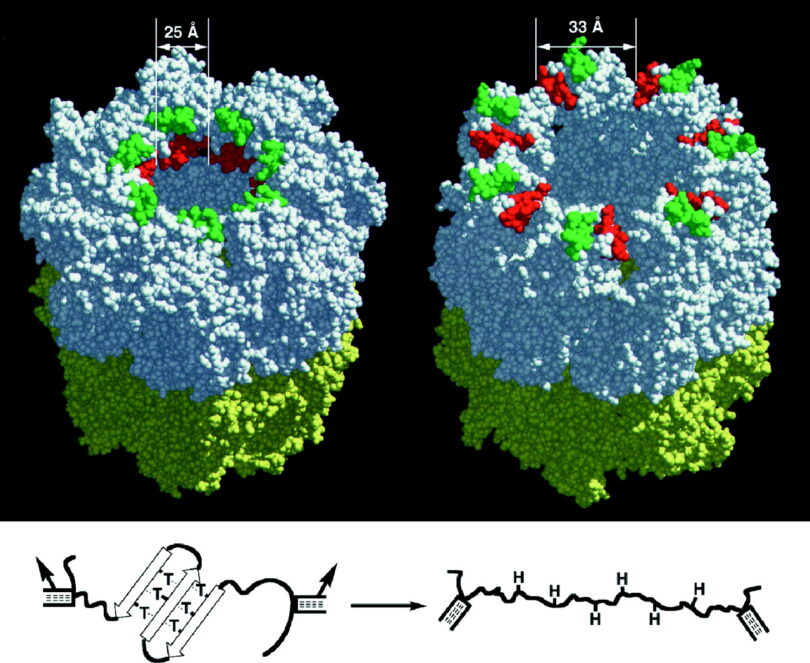
Nielson-Marsh, Christina, et al., “Biomolecules in fossil remains: Multidisciplinary approach to endurance,” The Biochemist, 12-14, June 2002
Last year, researchers estimated that the half-life of DNA — the point at which half the bonds in a DNA molecule are decayed as 521 years. ”
http://mathcentral.uregina.ca/beyond/articles/ExpDecay/Carbon14.html
The half-life of DNA is shorter than even Carbon 14 (half life of 5,730 years- 10 times longer than DNA) which is only considered valid on samples up to about 50,000 years old. Apply this to DNA with a half life of 521 years and DNA decay should be valid only for samples of about 5,000 years as a maximum!
Any article or scientific claim regarding the discovery of DNA in any fossil or sample indicates scientifically that the sample is less than 125,000 years old and such a claim is FALSE.
In light of the observable half-life of DNA decay, any conclusion regarding fossils (or any sample) which contains DNA and is also purported as also being greater a few thousand years old as factually invalid.
DNA delays at a known rate, therefore such time limits renders conclusions that both the sedimentary layers and the fossils within them are (as a maximum) 125,000 years old. Finally, because decay rates are observable in the present and rock layers which contain the fossils are not observable– the dating should be ruled by the half-life of DNA and not based on evolutionary time scales of millions of years.
Therefore these claims below (and many, many others) are falsified and debunked as “ancient” DNA:

https://www.seeker.com/worlds-oldest-known-dna-discovered-1764980841.html
https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2017/01/scientists-retrieve-80-million-year-old-dinosaur-protein-milestone-paper
(Mary Schweitzer’s) papers have the potential to transform dinosaur paleontology into a molecular science, much as analyzing ancient DNA has revolutionized the study of human evolution.”
https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2017/01/scientists-retrieve-80-million-year-old-dinosaur-protein-milestone-paper

https://www.livescience.com/23861-fossil-dna-half-life.html

By extracting gene fragments from insects preserved in amber for up to 40 million years, two independent teams of scientists have obtained the oldest DNA ever recovered from fossils.
https://www.nytimes.com/1992/09/25/us/40-million-year-old-extinct-bee-yields-oldest-genetic-material.html

Read more: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/million-year-old-rhino-tooth-provides-oldest-dna-data-180973117/#URcQVjLmY34JJPHr.99

Researchers in 2016 salvaged about 50,000 base pairs of genetic code from fossils excavated from a Spanish cave.
http://discovermagazine.com/2017/jul-aug/ancient-dna