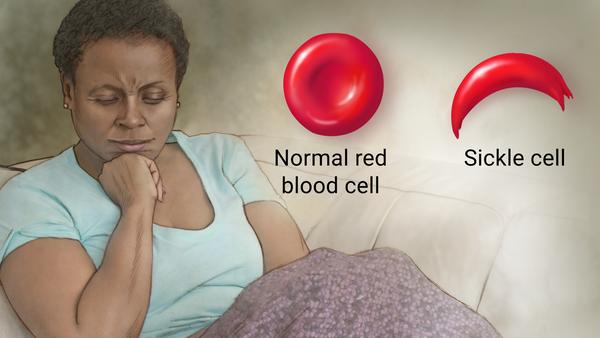
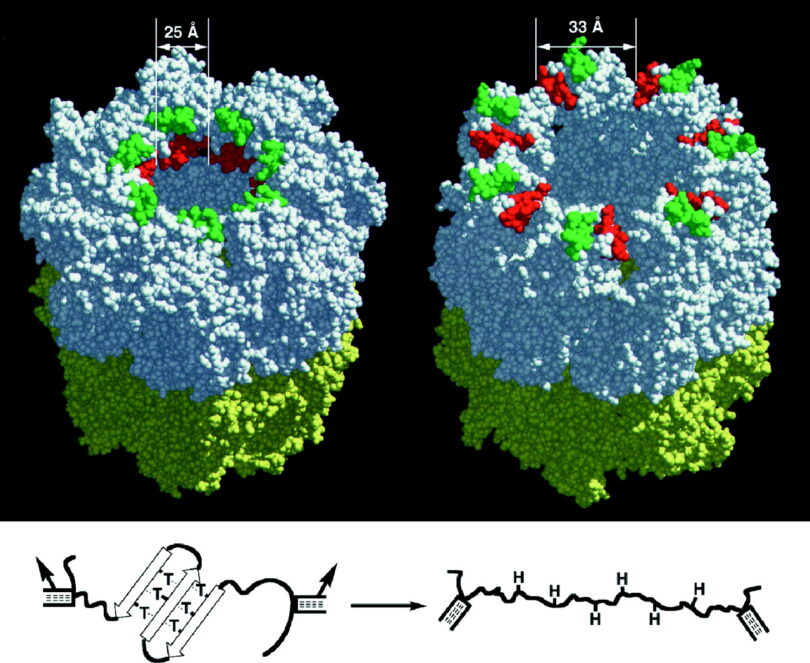
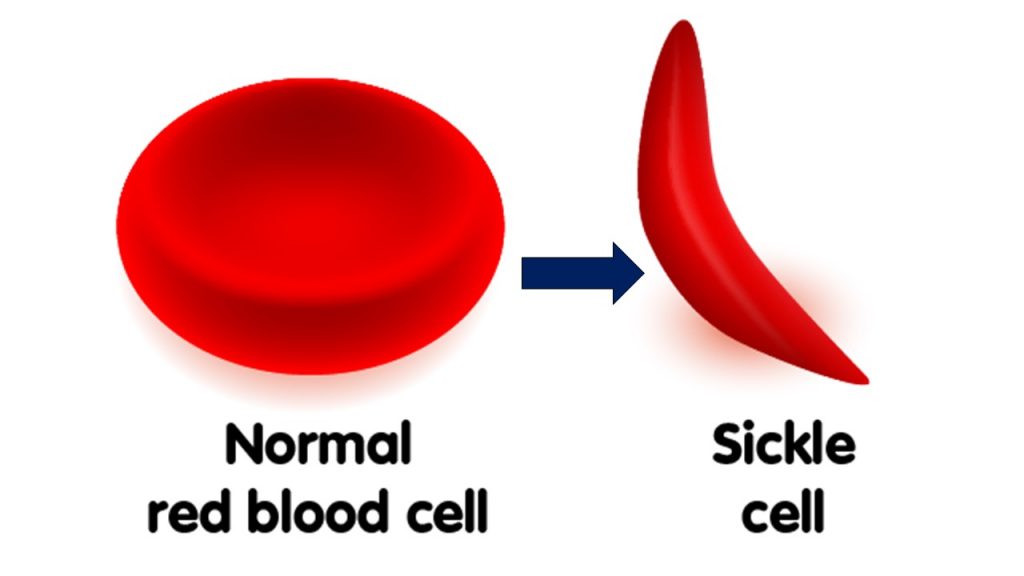
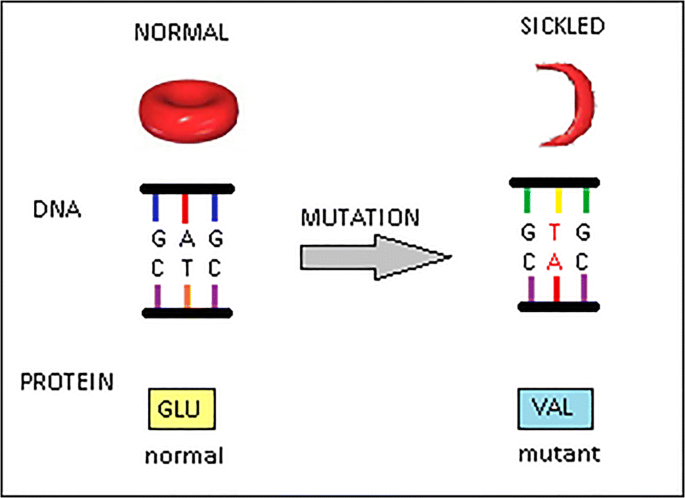
The hypothesized mutation that caused sickle cell is thought to have first occurred over 7,000 years ago. -1 The hypothesis of Neo-Darwinian Evolution hinges upon such new sequences forming in the germline by a random mutation; in this case, the mutation caused the normal round red blood cell to misfold the protein (red blood cell) into a “sickle” shape.
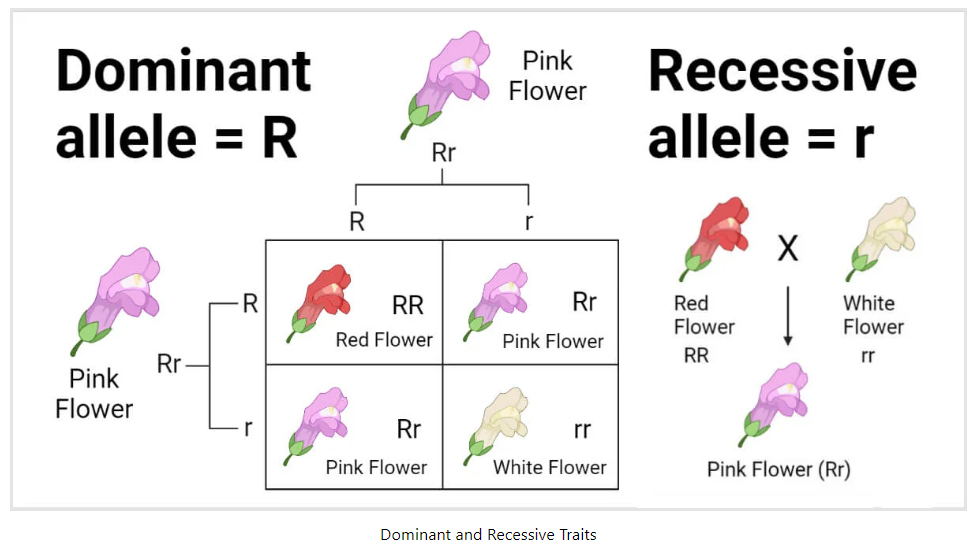
Allele frequencies of traits: Dominant or Recessive
Today, humans can carry both shapes of red blood cells, which can be observed in any blood sample. However, sickle-shaped red blood cells usually constitute less than 1% of all blood cells in those that do not carry the trait. However, as a survival genetic expression, round red blood cells can temporarily take on a sickle shape under certain conditions, such as extreme physical exertion, high altitudes with low oxygen levels, and other conditions. However, the extreme effects of Malaria rapidly caused the distribution of normally recessive sickle-shaped blood cells to become vastly unbalanced, reversing to a dominant germline trait.
Sickle Cell proliferated as the once rare and recessive sickle cell trait and rapidly became dominant. While sickle-shaped cells are thought to have existed in the human germline for well over seven thousand years, the effects of Malaria were unprecedented and detrimental. -2 Malaria did not cause the supposed mutation because the trait had preexisted in the germline for a long time, but the disease did cause the occurrence of the expansion of the normally recessive allelic trait of sickle-shaped red blood cells by Natural Selection: Those with the trait lived, those without it died.
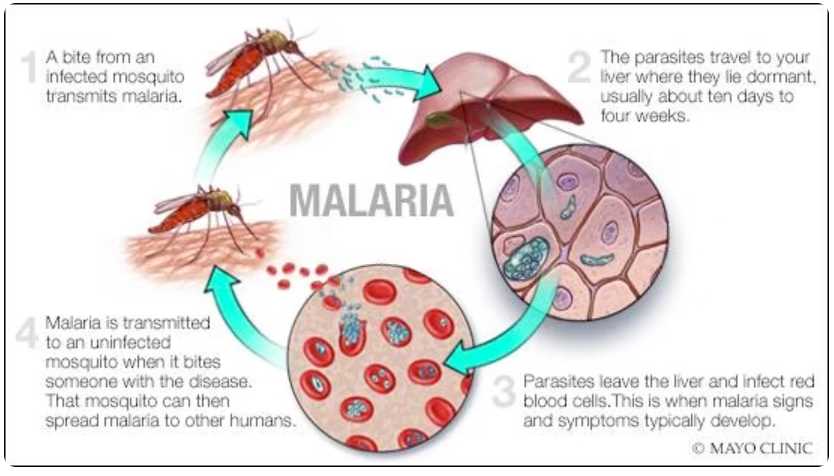
What causes Malaria?
The prevalence of sickle cell traits emerged during a very dark time of mass death rates caused by a parasite delivered by mosquito bites. These mosquitos carried parasites that were passed to human beings when they bit. These parasites are common in many tropical regions worldwide. After the mosquito bites, the parasite is introduced into the bloodstream, rapidly consuming and exponentially replicating. Using the round red blood cells as food and an incubator for reproduction. This explains why Malaria was so deadly and terrifying, with many dying within 24 hours of infection.
The “GOOD”
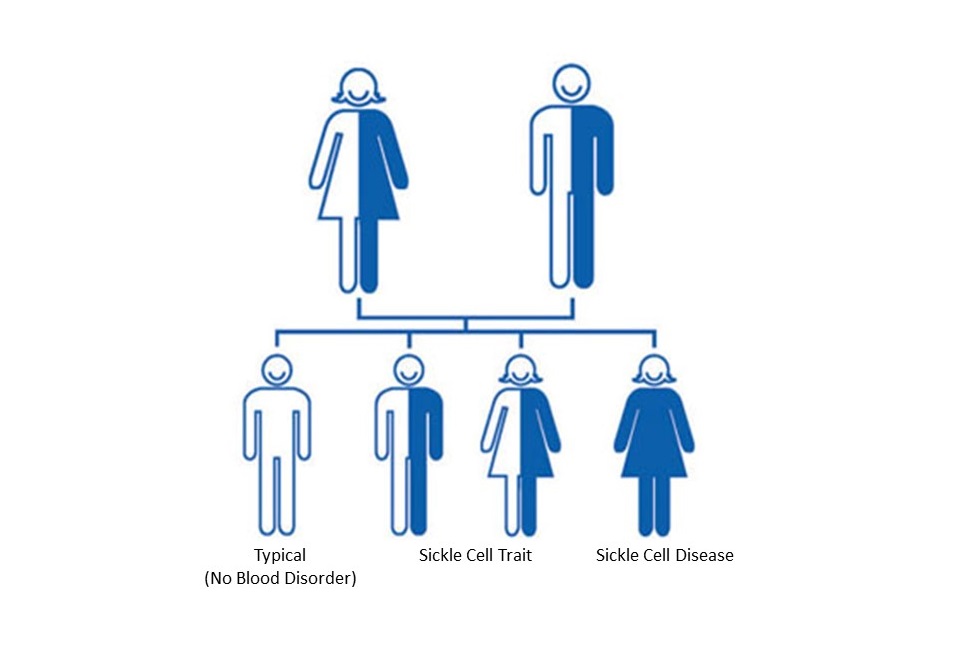
Fortuitously, those born with the rare sickle-shaped blood allelic trait did not die because the parasites only fed on round blood cells, and the sickle-shaped cells were invisible. The parasite did not recognize sickle red blood cells as food. Therefore, the recessive carriers of the sickle blood trait survived the plague of Malaria and reproduced. As survivors, both males and females carried the trait that translated into the offspring being a carrier. Now, both allelic gametes passed to offspring were sickle cell dominant.
Traits pass by hereditary functions- NOT by mutations
Any trait that can be passed to offspring first must exist in the parent’s sex cells as gametes. Each genetic option has just one corresponding allele trait. A trait such as eye color like variants for blue, brown, green, etc. Each genetic option has one allele gene variant. The rate at which these allele variants are expressed is called allele frequencies. Allele frequencies are more commonly referred to as dominant or recessive traits.
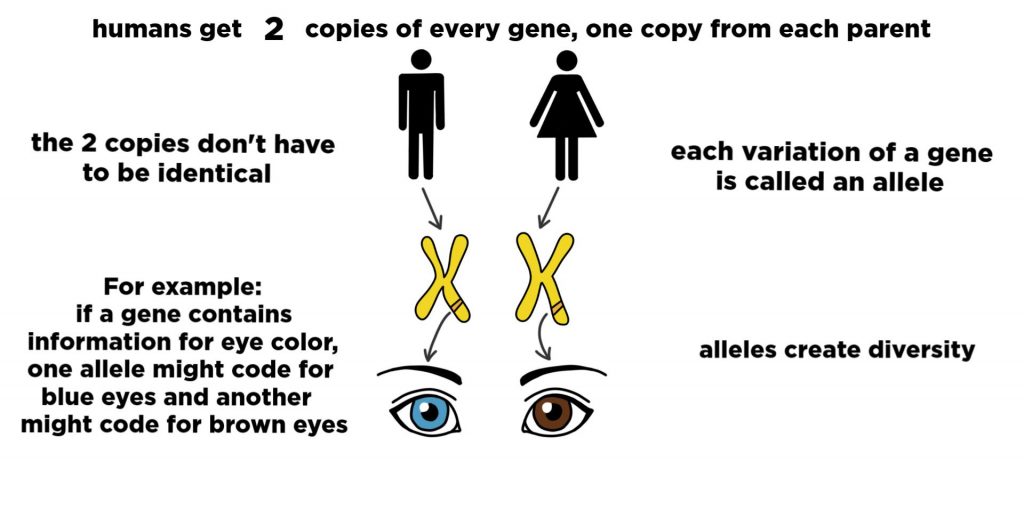
It is vitally important to emphasize that these allelic gene variants do not function by mutation but by hereditary function.
Evolution hypothesizes that these beneficial variants were originally formed by mutations. Recall that Sickle Cell was thought to have formed as a germline mutation more than 7,000 years ago.
First, this supposed germline mutation was never observed because we did not have laboratories and microscopes thousands of years ago. Second, while finding genetic evidence in fossils is surprisingly common, the genetic material is fragile, fragmented, deteriorated, and vastly incomplete.
One cannot substantiate the original “pre-mutational” allelic germline sequences to demonstrate when the first mutation occurred. They can only infer this claim.
Therefore, the Neo-Darwinian hypothesis of an ancient mutational formation behind the sequence that caused the sickle cell allele trait to emerge in the germline simply cannot be substantiated by modern genetic or fossil evidence. The hypothesis of a mutational emergence of this or any allelic trait is merely an inference.
Side effects
Sickle Cell Anemia is an inherited hereditary blood disorder (disease) known to cause severe compilations. This condition is notable as causing rigid, sticky, and misshapen (deformed) red blood cells. Some of the side effects of this disease include Acute Chest Syndrome, stroke, learning disabilities, heart problems, kidney problems, and other degradative conditions, including anemia, pain, swelling of hands and feet, increased rates of infection, delayed puberty or growth, pulmonary hypertension, multiple organ damage, loss of body water in urine, blindness, leg ulcers, gallstones, priapism (obstruction of blood vessels in the penis), and other vision problems. -3 Symptoms include fever, pale skin, yellowing (jaundice) eyes, stroke, trouble walking, confusion, and more. -3,4 Sickle Cell also increases blood pressure and blood clots, especially during pregnancy complications, including increased miscarriage, premature births, and low birth weights. -3,4 Other complications associated with Sickle Cell include predisposition to dehydration, chronic kidney disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, the slightly higher relative risk of pulmonary embolism, splenic infarction, acute chest syndrome, retinopathy, traumatic hyphemia (moderate quality evidence) for low pediatric height and weight, as well as heart failure (cardiomyopathy), and stroke. -4 Individuals affected by sickle cell disease are chronically anemic and often experience significant damage to their heart, lungs, and kidneys.” -3,4
In conclusion
The expression of the recessive sickle cell red blood cells derived from native germline traits saved many millions of lives. Unfortunately, it was only at the expense of an endemic disease that can never be removed from our genome. So much for evolution dropping “all that is bad.”
We discovered that the allelic variant for Sickle Cell preexisted in our native germline sequences, supposedly for thousands of years. Any mutation that caused this condition was not observed and cannot be substantiated by genetic evidence, including fossils.
Intelligent Design application
How do I explain Sickle Cell if it did not emerge by a mutation? As a Creationist, I am convinced that God created all life forms as fully mature in the beginning. God called creation “very good.” This likely means the genetic code had no mutations. There were no toxins in our food or environment. This equated to much longer (Biblical) lifespans. As germline mutations have accumulated, these have observably caused thousands of genetic diseases and suffering. Our life expectancy continues to decline despite modern medicine and technologies. My answer to how Sickle Cell emerged is by design and foresight of God. He made our genetics have an amazing ability to replicate with fidelity. The sickle-shaped red blood cell was designed for emergencies, like extreme exertion or oxygen deprivation. Turns out that this recessive sickle germline trait provided survival for millions. This is not due to Neo-Darwinian evolution but is a praiseworthy testament to our Creator. We have discovered that intelligence is found at every layer of biology, and native germline variants exist, just as they do for all life forms, to help ensure our survival.
1-Esoh, Kevin and Wonkam, Amroise, “Evolutionary history of sickle-cell mutation: implications for global genetic medicine” Published in ‘Human Molecular Genetics’, Volume 30, Issue R1, Mar, 2021, Pages R119–R128, https://academic.oup.com/hmg/article/30/R1/R119/6103809
2- Serjeant GR. The natural history of sickle cell disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013 Oct 1;3(10):a011783. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011783. PMID: 23813607; PMCID: PMC3784812. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3784812/
3- Miller AC, Gladwin MT. Pulmonary complications of sickle cell disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Jun 1;185(11):1154-65. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201111-2082CI. Epub 2012 Mar 23. PMID: 22447965; PMCID: PMC3373067. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3373067/
4-Xu JZ, Thein SL. The carrier state for sickle cell disease is not completely harmless. Haematologica. 2019 Jun;104(6):1106-1111. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.206060. Epub 2019 May 16. PMID: 31097635; PMCID: PMC6545856. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6545856/