In this article we shall look to answer these and many other questions and perhaps open new questions that remain to be answered. We shall examine (i) what defines an organism as being alive; (ii) consider what is a virus; (iii) examine the three modern theories on the origin of viruses; (iv) compare and contrast the Darwinian “bottom-up” view of genetics with a “top-down” perspective of intelligent design; (v) finally, relying on scientific evidence, we shall propose a theory regarding the origin of viruses based on evidence under the worldview of Intelligent Design and Creationism.
WHAT MAKES AN ORGANISM ALIVE?
Genetics: Native Cells
Of course, living organisms include plants, insects, marine creatures, and land animals which include human beings. All living organisms are primarily constructed of cells synthesized by their genetic material. There are single-cell organisms such as a bacterium and there are multi-cellular organisms such as a human being. Most all Native Cells contain their own copies of DNA but, some do not such as Red Blood Cells. Either way, all cells are synthesized by the organism’s genetic information. We shall call these “Native Cells”.
Symbiotic Relationships: Foreign Cells
There are also living organisms that can independently by their own native cells but, these cells live within other organisms. These living organisms consist of cells and are Foreign to their host. We shall call these cells “Foreign Cells”. These cells are not synthesized by the hosts native genetic material, yet the Foreign Cells are detrimental to the survival of the organism. Such relationships of Native and Foreign Cells coexisting have been called a symbiotic relationship. In symbiotic relationships each organism (cells) depends on the other for survival. Such relationships are found throughout nature and within all living creatures on earth.
Examples of “Good” Foreign Cells. An excellent example of Foreign Cells are bacteria. Of course, there are ‘bad’ bacteria such as Salmonella which causes food poisoning. There are also good bacteria such as humans use for digestion. Human Beings rely on such good bacteria, in fact, we could not survive without them.1 Such good bacteria cells constitute a staggering 57% of a human being’s total cell count. Therefore, 43% of all cells in a human being are Native Cells and 57% are Foreign Cells.
Non-Cellular material: Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
In addition to Native and Foreign Cells, in multi-cellular organisms, there are also non-cellular materials called The Extracellular Matrix or ECM’s. These materials are found in all life forms. These non-cellular components are synthesized by the Native organism’s genetic material. ECM’s are created when other cells release materials into extracellular space. They are found in all solid tissues such as muscles or even as a biochemical barrier such as a membrane for the cell to sit upon or as a means of adhesion to other cells. These non-cellular materials provide many other vitally important functions for living organisms including mechanical support, a medium for wound healing, and even calcification for teeth and bones.2 Examples of ECM material’s include Collagen (used for bones, skin, tendons, and ligaments), Elastin (used for muscle flexibility, lungs, tendons, skin, and ligaments), Enzymes (including protein synthesis and folding), Pectin (for cellular wall strength), and various Glycoproteins (used for purposes including amino acid adhesion during protein synthesis in the Ribosome). Bottom line, ECM’s support the function of surrounding cells and are required for survival of all living things.3
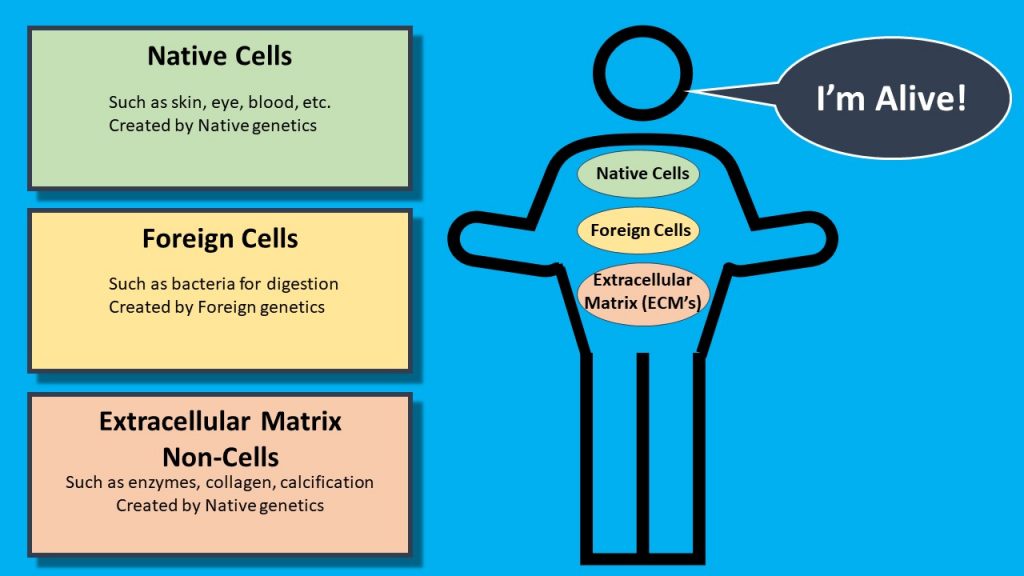
Living organism built of three things: Native Cells, Foreign Cells, and ECM’s
Together, the three materials we discussed above constitute a living organism. First, what we coined as Native Cells. Those cells synthesized by the instruction of the native organisms own genetic material, Second, living things have what we coined as Foreign Cells. Those cells that reside within a host generally within a good (though not always good) symbiotic relationship. Third, living organisms also are comprised of ECM’s. ECM’s are non-cellular material that is synthesized by the Native organism’s genetics. Based on which components you include in defining what is alive will result in different conclusions. How does a virus compare to other living (or non-living) things?
Viruses compared to Human Blood Cells. Before we begin to unravel what a virus is, or attempt to determine whether a virus is alive or not, let’s compare it to the human red blood cell. Are human red blood cells alive? Most all scientific journals, medical textbooks, and biblical Christians all say yes! Of course, there are a few that could argue that no they are not alive—like viruses—depending on what your definition of life includes. We find red blood cells to be alive despite the reality that they, like viruses, are missing molecular machinery. Of course, a human red blood cell cannot survive apart from a “host” but clearly it can be donated to another person. Surprisingly most all cells in the human body have DNA, however, red blood cells do not carry a copy of DNA. Red blood cells are manufactured “indirectly” by DNA informational genetics. Viruses also are missing molecular machinery. Viruses are missing massive molecular machinery, nearly all organelle required, however they do carry a copy of genetic material (either DNA or RNA).4 The production of red blood cells are synthesized by genetics indirectly, in that they do not carry their own copy of DNA. Viruses carry genetic material to replicate themselves but are missing essentially everything else.
Native ECM’s source of original viruses?
Could useful and protective native ECM’s be the original source of viruses? We found that red blood cells are synthesized as ECM’s indirectly using the genetic material of the living organism. Scientists have discovered native “viruses” in our genetic material. Could this be a clear clue as to where Foreign Viruses might have emerged by mutation? How they may have originated as a useful and protective ECM produced by the organism’s genetics. Later, mutational copy errors allowed a harmful or even deadly virus to become contagious. Such harmful and deadly viruses are unique and unlike any living or non-living thing on earth. What is a virus?
WHAT IS A VIRUS?
What is a Virus?
A virus is a microscopic organism that “infects” other living creatures including plants, animals, and even bacteria (called a bacteriophage). Viruses are found in virtually every living organism, within every ecosystem on Earth 5. There are more than 5,000 different known viruses to date, 5 most are harmless to human beings. Viruses can infect the same species, or they can cross over to other species. Viruses are not like Foreign Cells because they are not cells and they lack significant molecular machinery. Viruses, however, do have their own genetic material either DNA or RNA. Due to not being a cell and missing significant molecular machinery, viruses cannot survive independent of a living host. Foreign viruses infect a host. These viruses parasitically steal the cellular function they lack as to complete their own reproduction and survival. Useful viruses can be native to the organism and even generated by genetic material.
Of course, there are cases where viruses have become harmful and even deadly, although contrary to what you might believe, such cases are exceedingly rare. Viruses that have become deadly have been spread when different species infect a human being. As an example, birds, pigs, monkeys, and even bats have had viruses that crossed species into humans. Such viruses have included the recent Corona-virus (Covid-19), Influenza’s, Ebola, SARS, MERS, Smallpox, Measles, Malaria, and HIV. These deadly viruses are exceptions and not the rule on how most viruses operate. Scientist estimate that there are millions of different undiscovered viruses that are not transmittable or harmful to humans.
A Virus is not a cell then how does it survive?
A virus, as compared to a bacterium which is a cell, cannot perform homeostasis. A bacterium can survive independently provided it has food and an adequate environment while a virus cannot survive independently. When viruses were first discovered in 1892 by Dmitri Ivanovsky, he noted that these organisms lacked hallmarks of other living things. It was later determined that viruses do not directly carry out metabolic processes nor do they have the molecular equipment to reproduce themselves. No virus has ever been found that contains Ribosomes for protein production or ATP required for energy. In other words, viruses can only reproduce themselves inside a host cell that has all the needed molecular machinery. Because these foreigners are missing most all their molecular equipment (aside from their genetics) they simply cannot survive outside a host. Therefore, the virus enters a host and replicates itself by stealing function from the hosts existing cells as a parasite.
MODERN THEORIES ON THE ORIGIN OF VIRUSES
Three Theories on how viruses emerged
Of course, all these theories are extremely evolution friendly, despite many obvious contradictions and paradoxical implications their various hypothesis’s claim. The first theory is can be called “The Virus-first Hypothesis”.6 Never really considered a valid theory in the past, recent years have led evolutionary popularizers to warm up to this theory. They reason that perhaps viruses predated (or maybe co-evolved) with their cellular hosts back to the origin of first life.6 Under this theory, proponents state that viruses deserve their own line in Darwin’s Tree of Life. Early “roots” as Bacteria, Eukaryotes, or Archean. Perhaps viruses are the roots of these roots? The second theory is called “The Regressive or Reduction Hypothesis” which states that viruses emerged due to broken genetic material that became transmitted to a different species.6 This theory would tend to view a virus as once belonging to a fully functioning organism such as a bacterium that became “disabled” through damaging mutations. The third prominent theory is called “The Progressive or Escape Hypothesis. This theory states that viruses arose from genetic elements that “gained” the ability to move between cells.6 Clearly, these theories may have overlap, need to be combined, or perhaps, all three will be replaced altogether as more research data is gathered. However, as of today, science has determined no definitive answer or even preferred hypothesis as to how viruses first emerged.
DARWINIAN “BOTTOM-UP” GENETICS COMPARED TO “TOP-DOWN” OF INTELLIGENT DESIGN
Evolution and the Bottom Up view of life
The worldview of evolution maintains a belief of a “bottom up” view of living things today. This is illustrated by Charles Darwin in his book The Origin of Species. While evolutionists will point out the origin of life is distinctly separate issue from evolution, one must assume that if naturalism is fact, in the distant past life must have somehow emerged through purely from non-living chemicals. The bottom-up Tree of Life starts with “simple” celled organisms such as bacteria and imagines that through eons of time these organisms gain function. Climbing “upwards” from the roots by the sheer mechanism of natural selection. Even an elementary school child can recognize Darwin’s Tree. Where single cell organisms like cyanobacteria gain complexity and genetic material to become sponges. Then sponges to starfish, to worms, to marine plants, to shellfish, to fish, to land plants, to amphibians, to reptiles, to birds, to mammals, to apes, to mankind. Once the field of genetics began to be revealed these views of Darwin’s were updated. Often called “Neo-Darwinism” refers to the addition of previously unknown genetics and specifically spontaneous mutations as the mechanism causing change or the evolution of all species of animals. Logically, and perhaps why Darwinism was so quickly accepted, in nature it was obvious that the strongest reproduced and passed their heredity to future generations. By adding in mutations as the mechanism for such changes caused Darwinism to rely completely on such spontaneous mutations to result in beneficial changes in organisms. After all, it was spontaneous mutations that created every species of organisms on earth from bacteria to mankind. Therefore, Neo-Darwinism finds that spontaneous mutations of genetic material becomes “locked in” through reproduction called “natural selection”.
Creation and the Top Down view of life
The worldview of Creationism maintains a belief that God created life as fully formed creatures from the very beginning. Of course, there are Christians that maintain a mix that combines a variety of evolutionary and Creation principles and beliefs, but for our purposes here, we are ignoring such compromised positions. Creationism views life as a “top down” essentially the opposite of Darwinism. Creationism believes that the original created creatures received the highest function and ability from the beginning; There was never an increase or evolution of species as imagined by evolution such as fish to frogs. The Bible states that God created all living things during a six-day creation event. During this creation, all genetics where fully functional from the beginning. As life proliferated, as provided by genetic functions (of DNA Alleles). Reproduction permitted the vast variability we observe today within all life forms. Since the beginning, creatures remained the same “Kind” as the Bible states. As an example, Kind means that horses remained part of the horse family, but diversification occurred over thousands of years. Today the horse family includes although horses, donkeys, zebras, etc. Kinds find that cats remain as cats, dogs as dogs, apes as apes, and humans were always human. This view recognizes natural selection as defined as hereditary function. However, Creationism believes there was never any change of Kinds. This perspective believes that mutations are not creative mechanisms that “build up” or “change kinds” but rather, mutations are genetic copying mistakes. These mistakes have largely caused havoc on living organisms despite the built-in error correction of DNA.
THE ORIGIN OF VIRUSES FROM AN INTELLIGENT DESIGN PERSPECTIVE
Recap
Recall our coined terminology in which all living creatures are composed: (1) “Native Cells” are those proteins synthesized by the organisms unique genetic material; (2) “Foreign Cells” reside within a host from a foreign organism and are not synthesized by the organisms unique genetic material. These cells can and often exist in a symbiotic manner where each relies on the other for survival. (3) ECM’s (Extracellular Matrixes) are non-cellular materials which were synthesized by the Native organism’s genetic material which are required for survival by the organisms. ECM’s all lack components of the living cell. ECM’s include all the purposeful viruses used by organisms either generated by Native Cell genetics or by Foreign.
Recall the three primary theories regarding the emergence of viruses: (1) “The Virus-first Hypothesis” states that viruses predated first life or perhaps co-evolved with their cellular hosts; (2) “The Regressive or Reduction Hypothesis” states that viruses emerged due to broken genetic material that once belonged to a fully functioning organism but became “disabled” through damaging mutations. (3) “The Progressive or Escape Hypothesis” states that viruses arose when genetic elements “gained” the ability to move between cells and even to different species. Modern science recognizes none of these as the clear answer and finds it likely that these theories should be combined or perhaps eliminated if future data dictates otherwise. We concluded that as of today, science has determined no definitive answer or even preferred hypothesis as to how viruses first emerged.
Darwinian “Bottom-up” in light of evidence
We found that evolutionary theory views life originating first by a mysterious happenstance beyond the scope of this article. For our purposes here, life must have emerged when non-living chemicals began to interact with each other in unprecedented ways. Somehow, purely through scientific physical laws the first replicating life form originated. This perspective lacks observable genetic empirical data and relies on speculative bodies of evidence such as homology, fossil records, conjecture, or a combination of these. Evolutionists believe that generation to generation, built of hundreds of millions of years, the mechanism of spontaneous random mutations locked in by the “blind guiding hand” of natural selection constructed “simple” life forms such as bacteria into multi-cellular organisms such as mammals. These mechanisms are responsible for both the physiological (matter) and genetic information (non-matter) entities necessary for life. The theory assumes that such blind processes have continued for approximately three billion years, constantly increasing, and building diversity and genetic information. This “bottom-up” view has resulted in all the vast diversity of species on earth: bottom simple organisms to the top where human beings reign.
Intelligent Design “Top-Down” in light of evidence
In contrast, the intelligent design perspective assumes that originally created organisms both physiologically and genetically, from the very beginning, would be the purest. Logically, as generations pass via copies of copies of genetic material become compromised with errors. These copy errors (mutations) mostly cause harm or even death within all living species. This position would be incredibly surprised to find any beneficial mutation as the two terms are quite paradoxical. Empirical evidence related to mutational copy errors has supported these expectations. Counterintuitively, perhaps a few mutations such as Sickle Cell can be argued as a beneficial mutation but beyond this evidence is very scarce. This perspective expects to find genetics degrading over the generations and this is exactly what scientific research has found.
Mutating Viruses exhibit Top Down characteristics
Considering decades of scientific data and research that has illuminated the reality that spontaneous mutations cause damage we would expect this to also impact viruses. Therefore, our intelligent design perspective fully expects that broken genetics play a role in viruses. Perhaps not so much in native viruses or helpful viruses but more likely in harmful or deadly viruses. Mountains of genetic research holds to these realities. Mutations outside reproduction, are about 2/3 degradative or even deadly and about 1/3 neutral while the search for beneficial mutations are virtually non-existent.
The flu mutates each year: a poster child for evolution?
We all know that each year the medical field offers a new flu shot for that year’s strain. Why? Because the flu virus from the last year, massively killed by the prior year’s vaccine, mutated and this version survived. Are we saying that evolution is true then? You admit it mutated and became better? No—not better. It is actually worse. It lost or deleted or harmed its earlier genetic material as a sole means of survival. It certainly did not become something better and its genetic material is degraded. In fact, such evidence clarifies that this a means of building life on Darwin’s Tree must certainly be untrue.
Mutated viruses not good examples for “bottom-up” evolution
As we have discussed, viruses are not cells and are missing largely everything except genetic material they use to reproduce in hosts. Viruses have either a full double strand DNA, a single strand DNA, or in the worst and most deadly viruses only have RNA. Single strand DNA and RNA lack the incredible editing and correction software built into double stranded DNA. History has shown that some of the most endemic viruses (those that continue to come back each year) use only a single strand DNA or merely RNA which result in unregulated mutation over millions of pairs of genetic material. Also, because viruses MUST survive within the host to survive—they MUST mutate or face complete elimination. Such degradation and struggle for survival against killer antiviral vaccines does not create an “upward evolutionary” process of species. Rather, the mass death of viruses allows by default, counterintuitively, those mutated strains to multiply and survive for next year. Of course, any search for beneficial characteristics that were passed to later offspring amount to nothing more than limping over the finish line and survival into the next flu season. Viruses mutate due to a lack of controls, with millions of base pairs in their genetics, while being slaughtered by anti-viral vaccines where only the strange mutants survive. If this is a grand example of how Darwinian “bottom-up” evolution works then this theory has many, many more problems then it has solutions.
CONCLUSIONS & OPINIONS
Conclusions from a creationist perspective
Let’s bring it all this together from an intelligent design and creationist perspective. First, we would expect to find that all living things were created from the beginning in the purest and most perfect form. We were created with antibodies as protection from viruses both from other human beings as well as potentially from other species. From the great quantities of good viruses including some ECM’s it would be fully consistent to expect the original creation to include viruses. Logically, with the presence of a dynamically complex immune system this was created for a purpose from the beginning– to deal with viruses which must have also existed from the beginning.
Could viruses have emerged from mutated ECM’s?
What about all those millions and millions of helpful (neutral or harmless) viruses that are used by living things of every variety? Some are native genetically and some come from foreign. What does the existence of most all viruses as useful and only a scant few as harmful and even less as deadly? Could it be that harmful viruses which are adequately mitigated by the built-in defense of our immune system have always existed? What about those fractionally few deadly viruses which our immune system could not stop that cause death and destruction?
Perhaps viruses emerged from broken cells
As another possibility at to an explanation for the emergence of virus might have originally began as a cell was broken and stripped of essentially everything but the nucleus and the genetic information. All known viruses carry genetic information (DNA or RNA) which is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells (all animal and insect cells). The nucleus is also very small representing only about 10% of the total cell volume in eukaryotic cells– still much larger then most viruses but still a possibility. Some evolutionary models propose that the more “ancient” cells (eukaryotic cells are those without membranes), like modern day viruses infected other eukaryotic cells. As generations passed, the theory goes, that these “viruses” became permanent residents and ultimately caused the rise of eukaryotic cells. From an intelligent design and creationist perspective (where all the various life forms were created from the very beginning) the theory that perhaps some of the modern day viruses, especially those harmful or deadly varieties, were indeed remnants of a broken cells. Perhaps of eukaryotic cells that became stripped of essentially everything except its nucleus or even perhaps as bacterial infections or poisonings from plants or fungus entered into multi-cellular organisms from prokaryotic organisms. In either case, perhaps a once fully functioning cell became disabled by massive mutational genetic losses. This makes sense as the only way the first viruses could have survived as to have been inside a host from the very beginning.
What about harmful or deadly viruses?
Did God create harmful and even deadly viruses from the beginning? Even in consideration of the vast limitation of human intellect, we must clearly state that of course, we could never “know” Gods intensions, designs, or purposes. We certainly should never argue that “God wouldn’t do it that way.” What does the evidence reveal? Did God create deadly viruses from the beginning? We think not.
Viruses have a chicken or the egg dilemma for emergence
We find all life forms operating by dynamically complex molecular machinery which works by genetically derived specificity and purpose. Science has called many of these wonderfully orchestrated operations that are interdependent and could not have arisen in a step by step process as imagined by Darwin to be irreducible complex systems. Such systems lend evidence that all these various components must have been working from the very beginning. Creation and intelligent design effectively answer the chicken or the egg dilemma–the fully functioning chicken came first. Therefore, logically, in consideration of a top down model of Creation, things were best at the time of creation and have degraded as more copies were made. Errors such as those caused by spontaneous mutations accumulate in the genetic material of all living things and are driving genetic entropy.
The origin of viruses
First, we find that the emergence of viruses roughly line-up with the “broken genetics” theory or “The Regressive or Reduction Hypothesis”. We also could partly line up with the escape theory of such broken genetics– the two are closely related. However, we do not find that such broken genetics emerged via a once fully functioning independent foreign organism which later became disabled by mutation. We more believe that native cells or ECM’s where the likely cause of such viruses. These were anticipated within creation as evidenced by our immune system. Ultimately it would reason that the original form must have been native because without the needed molecular machinery it would have perished. How to imagine this first forming independently creates a paradox and chicken or the egg dilemma. Therefore, evidence points toward viruses emerging originally from Native Cells or ECM functions which became compromised due to random copying errors or spontaneous mutations. These causes were degradative. Finally, original compromised and mutated viruses became contagious to other organisms that also lacked preexisting immunity to fight it.
Second, considering the many beneficial Native genetic functions within all living things including both cellular and ESM’s we therefore theorize that viruses must have been part of the original creation. Perhaps original viruses were propagated by Native Cell operations derived for useful and protective purposes as synthesized from the genetic material of the Native life form. Logically, this would also be true for Foreign cells and perhaps for symbiotic relationships as well. As these originally created viruses reproduced for useful and protective purposes, like all genetic material, accumulated copy errors which eventually led toward harm.
In our opinion, this maybe how deadly viruses first emerged. We imagine a compromised genetic capsule of once useful ESM’s compromised by mutation. Eventually, due to exposure to populations in the environment, these compromised ESM’s became contagious. At first they were contagious to those of the same species as in the common cold. Later, such viruses became contagious crossed species such as from bird to human. While our immune system could do well against same species contagions and many others, when rare cross species contagions infected the host deadly affects happened. Perhaps because these novel viruses that crossed over species certainly had never been experienced by the immune protectors before.
Finally, once useful, and protective viruses emerged as a deadly virus such as we can encounter today. Just as malformed amino acid chains (due to spontaneous mutations) cause somatic cancers, so can these viruses cause death and harm. While perhaps never intended as such by God’s original creation, this does not mean that it was unexpected by God as evidenced by warnings of such pestilence. It is our theory that viruses are the result of a top-down creation where genetics are winding apart.
1 Bacteria and Humans – Beneficial and Harmful Relationships
2 British Society for Cell Biology “Extracellular Matrix and Cell Adhesion Molecules”
3 Khan Academy “The extracellular matrix and cell wall”. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/structure-of-a-cell/cytoskeleton-junctions-and-extracellular-structures/a/the-extracellular-matrix-and-cell-wall
4 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21523/
5 “Viruses” C Michael Hogan; Encyclopedia of Earth
6 “The Origins of Viruses; How did viruses evolve? Are they a streamlined form of something that existed long ago, or an ultimate culmination of smaller genetic elements joined together?” By: David R. Wessner, Ph.D. (Dept. of Biology, Davidson College), 2010 Nature Education Et.al Wessner, D. R. (2010) The Origins of Viruses. Nature Education 3(9):37 https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/the-origins-of-viruses-14398218/